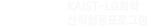- 주소
대전 광역시 유성구 대학로 291 학국과학기술원 응용공학동 W-1 2406호, 실험실 5407호
- 전화
042-350-3314
- 이메일
- 홈페이지
- 약력
- B.S. Materials Science & Engineering, SNU (2004)
- Ph.D. Materials Science & Engineering, MIT (2010)
- Postdoctoral Scholar, Materials Science, Caltech (2010 – 2013)
- Assistant Professor, Materials Science & Engineering, KAIST (staring 2013.02)
연구실소개
Sustainable Energy Materials Laboratory(SEML)에서는 태양에너지를 효율적으로 이용하여 유용한 화학연료를 합성(Solar Fuels)하고, 이를 다시 전기에너지로 변환(Fuel Cells)하는 과정을 연구합니다. 이것은 저탄소, 지속가능한 미래의 에너지 시스템으로 나아가기 위한 핵심기술입니다. Solar Fuels 및 Fuel Cells의 에너지 변환과정 중 계면에서 일어나는 열화학적, 전기화학적 촉매 반응들은 전체 device의 효율과 성능을 결정합니다. 우리 연구실에서는 계면에서의 다양한 반응들을 보다 정량적으로 이해하고, 이를 통해 새로운 물질과 구조를 설계합니다. 그리고 다양한 나노구조 공정기술들을 통해 이를 제작합니다.
연구내용
태양열발전과 열화학반응을 결합한 차세대 화학연료 합성 (Solar-driven Thermochemical Fuel Production)
태양열에 의한 열화학반응을 이용하여 수소와 다양한 화학 연료들을 합성하는 기술은 차세대 고효율, 대용량 에너지저장기술로 큰 주목을 받고 있습니다. 우리는 현재까지 알려지지 않은 새로운 촉매물질과 구조를 개발하고 있습니다. Useful, chemical fuels can be produced through a thermochemical process driven by solar energy. This strategy relies on the capacity of selected nonstoichiometric metal oxides to release and uptake oxygen in response to changes in temperature, where the thermal cycling is induced by exposure to solar radiation. The resulting stoichiometry changes can be directly utilized for fuel production when coupled with the introduction of appropriate reactants gases such as H2O and CO2.
고온 연료전지 전극 설계 및 제작 (Next Generation Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Electrodes)
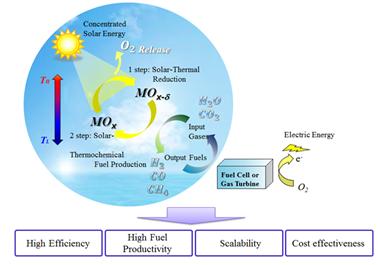
고체산화물연료전지는 화학 연료를 전기 에너지로 변환해 주는 현존하는 가장 효율이 높은 기술입니다. 우리는 고성능 전극 제작을 위한 새로운 물질과 구조를 찾고 있습니다. Essential to the fuel cell energy conversion process are the electrochemical reactions at the electrodes - oxygen reduction at the cathode and fuel oxidation at the anode. To rationally develop novel and highly active electrode materials, we do experimental and theorical investigation through simplified, well-defined model systems and obtain basic insights to make rapid transport properties of both ionic and electronic species and favorable electro-catalysis. We also fabricate high performance fuel cell electrodes by means of advanced nano/micro-fabrication tools.
나노 스케일 전기화학 촉매 개발 (Nano-scale Phenomena in Electrochemical Catalysis)
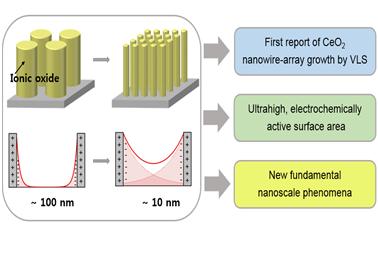
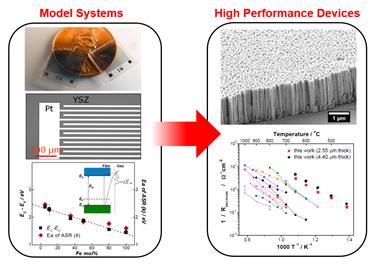
산화물 촉매의 전기화학반응은 다양한 에너지 변환 및 저장 장치들의 핵심 반응입니다. 우리는 나노구조를 이용하여 새로운 개념의 촉매를 개발하고 있습니다. We aim to uncover new phenomena in electrochemical catalysis when material dimensions are on the nanoscale. Through precise control of space charge overlaps at surfaces of ionic solids with aid of advanced nano-fabrication techniques, we will explore the influence of space charge effects on surface catalytic properties, targeting high performance electrochemical devices including fuel cells, electrolyzers, batteries and sensors.
연구성과
Uncovering new nanoscale phenomena in electrochemical catalysis (2013. 9 - 2015. 8)연구내용
- 본 연구는 이온고체물질(ionic solid) 표면의 space-charge효과를 정밀하게 측정 및 조절하여, 나노스케일에서 일어나는 새로운 전기화학적 촉매현상의 발견을 목표로 한다. 이를 위해 다양한 크기와 조성을 가지는 정렬된 나노와이어 구조의 촉매물질을 제작하고, 표면의 전기화학적 특성을 측정 및 분석한다.
- -최신 기법들을 활용하여 뛰어난 결정성과 높은 종횡비 및 패턴선명도를 가지는 정렬된 나노와이어 구조체를 제작
- -특수 설계된 측정셀 구조를 이용하여 물질 표면의 전기화학적 특성 측정
- -정량 수치 계산법을 응용한 데이터 분석
기대효과
- 연료전지, 전해조, 센서 등과 같은 전기화학 응용분야 기술적 돌파구 제공
- 정렬된 세리아 나노와이어 구조로 high activity 연료전지 전극 제작
- 새로운 CeO2 나노 와이어 구조 제작기법 제시
연구내용
- 새롭게 주목받고 있는 혼합전도성 환원전극 소재들의 활용 가능성을 파악하기 위하여 핵심 전극물성 및 반응기구를 정량적으로 분석한다. 이를 위해 박막증착, 패턴기술 및 다양한 측정기법을 종합적으로 사용한다. 또한 3차원 설계모델 개발과 나노공정을 통해 전극반응을 극대화할 수 있는 나노구조를 설계 및 제작한다. 추가적으로, 금속나노입자의 sintering 제어기술 개발을 통해 고온환경에서 열적/화학적 안정성을 갖는 신개념 금속-나노촉매 시스템을 개발한다.
- -차세대 혼합전도성 환원전극 소재 선별 및 핵심 전극물성의 정량적 규명
- -환원전극 성능 극대화를 위한 나노기반 구조의 설계 및 제작
- -고온 작동형 금속-나노입자를 활용한 새로운 전극시스템 개발
기대효과
- 분자에너지 변환 동종/표면반응 특성 데이터베이스화 및 정보 제공
- 반응기구 분석을 통해 분자에너지 변환 기구에 대한 이해 증진
- 미래 청정 에너지원으로 주목받고 있는 연료전지의 상용화를 앞당겨 연료전지 시장에 유리한 고지를 선점
대표 논문
- W. Jung, K.L. Gu, Y. Choi, and S.M. Haile, "Robust nanostructures with exceptionally high electrochemical reaction activity for high temperature fuel cell electrodes," Energy & Environmental Science, (2014).
- W. Jung, J.O. Dereux, W.C. Chueh, Y. Hao, and S.M. Haile, "High electrode activity of nanostructured, columnar ceria films for solid oxide fuel cells," Energy & Environmental Science, 5 (2012).
- Y. Chen, W. Jung, Z. Cai, J.J. Kim, H.L. Tuller, and B. Yildiz, “Impact of Sr segregation on the electronic structure and oxygen reduction activity of SrTi1-xFexO3 surfaces,” Energy & Environmental Science, 5 (2012).
- W.C. Chueh, Y. Hao, W. Jung, and S.M. Haile, “High electrochemical activity of the oxide phase in model ceria-Pt and ceria-Ni composite anodes,” Nature Materials 11 (2012).
- W. Jung and H.L. Tuller, “Investigation of surface Sr segregation in model thin film solid oxide fuel cell perovskite electrodes,” Energy & Environmental Science 5 (2012).
- W. Jung and H.L. Tuller, “A new model describing solid oxide fuel cell cathode kinetics: Model thin film SrTi1-xFexO3-δ mixed conducting oxides – a case study,” Advanced Energy Materials 1 (2011).
- C. Solis, W. Jung, H.L. Tuller, and J. Santiso, “Defect structure, charge transport mechanisms, and strain effects in Sr4Fe6O12+δ epitaxial thin films,” Chemistry of Materials 22 (2010).